10ct Round Lab-Grown Diamond Cost Guide | Messi Gems
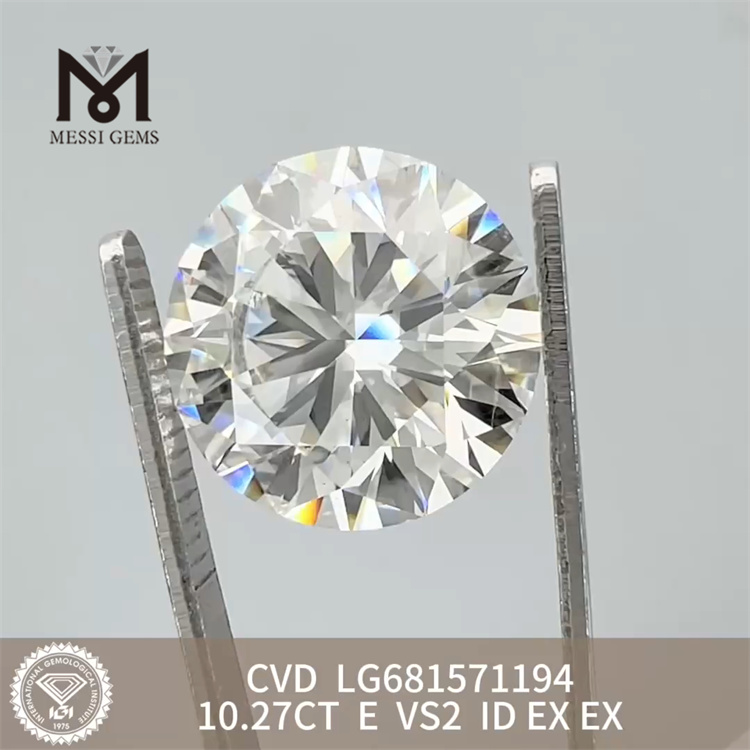


A perfect circle, engineered for light. When you search “10ct round lab grown diamond cost,” you’re really asking how much it takes to unlock precision, symmetry, and relentless sparkle at a scale that turns heads across a room.
Why round pricing is so cut-driven:
· Light return: Rounds are the most optimized shape for brilliance. Tiny deviations in pavilion/depth/table can alter performance—and price.
· Symmetry and hearts-and-arrows precision: True optical symmetry requires stricter tolerances, increasing labor and yield loss but rewarding with top sparkle.
· Diameter spread: At 10ct, diameter commonly sits ~14.5–15.5mm. Stones that “face up” larger for their weight often price higher.
New angle: think of the 10ct round as a “stage for light choreography.” The goal isn’t just brightness—it's rhythm. You want crisp, small flashes under daylight, bold fire under spotlights, and an on/off scintillation that reads clean even on camera. We’ll supply comparative light videos so you can see which stone’s “performance” speaks to you.
Setting strategies for big-round brilliance:
· Knife-edge solitaire in platinum to visually slim the band and spotlight the disc of light
· Cathedral shoulders for structural lift and elegance without bulk
· Bezel for a modern, wearable shield that adds a graphic halo of metal
· Hidden halos to increase perceived diameter while keeping the face minimal
Why lab-grown for 10 carats:
· Access: Precision cutting at scale without mined scarcity pricing
· Consistency: Easier matching for side stones or studs if you’re building a suite
· Ethics: Lower-impact provenance with contemporary traceability




About Weight
*One carat is equal to 0.2grams.
*The waist diameter of the diamond will be affected by the cutting method and proportion. So the same weight diamonds may have different waistlines.
CARAT&DIAMETER
0.10cts≈3.0mm
0.20cts≈3.8mm
0.30cts≈4.5mm
0.40cts≈4.8mm
0.50cts≈5.2mm
0.75cts≈5.9mm
1.00cts≈6.5mm
1.50cts≈7.4mm
2.00cts≈8.2mm

About Diamond Rough
COLOR: D E F G H I J
CARAT: 0.5-2.0
CLARITY: VVS VS SI
CUTTING: IDEL EXCELLENT


Make your personal jewelry
Ring, Earrings, Bracelet, Pendant with Moissanite/ lab grown diamond/Eemerald your personal jewelry maker.

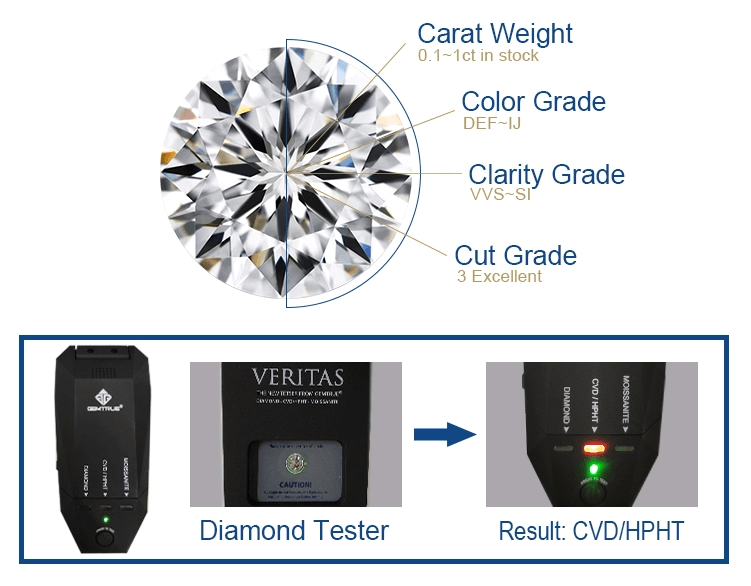
About Diamond Tester
As HPHT method involves using metal catalyst, it is hard to avoid some metals entering the crystal during growing process, so HPHT diamonds might be magnetic. And if the magnetism is too strong, diamonds will not be able to pass the diamond teste. Because CVD diamonds are formed by mere gas, they can be produced without magnetic and are able to pass the diamond tester pen.
What is cvd diamonds?
Chemical Vapor Deposition. Chemical vapor deposition uses one or more gases to chemically react on a heated solid substrate and is coated with a solid film. The diamond is a natural diamond bare stone as the mother stone, using high-purity methane, plus hydrogen, nitrogen and other gases to assist, in a microwave oven under high pressure, so that the same carbon molecules in methane as diamond continue to accumulate on the rough diamond. Layer by layer, it can form transparent diamonds up to 10 carats.
In order to make CVD diamonds grow smoothly, the carbon source is often methane that already has a diamond structure. Methane can be regarded as a monoatomic diamond extruded with hydrogen. The quality of this "grown-up" diamond is almost the same as a natural diamond, making it hard to distinguish with the naked eye. At present, this kind of CVD synthetic diamond can be distinguished from natural diamond by observing its phosphorescence performance under short-wave ultraviolet, and a simple preliminary screening can be performed.
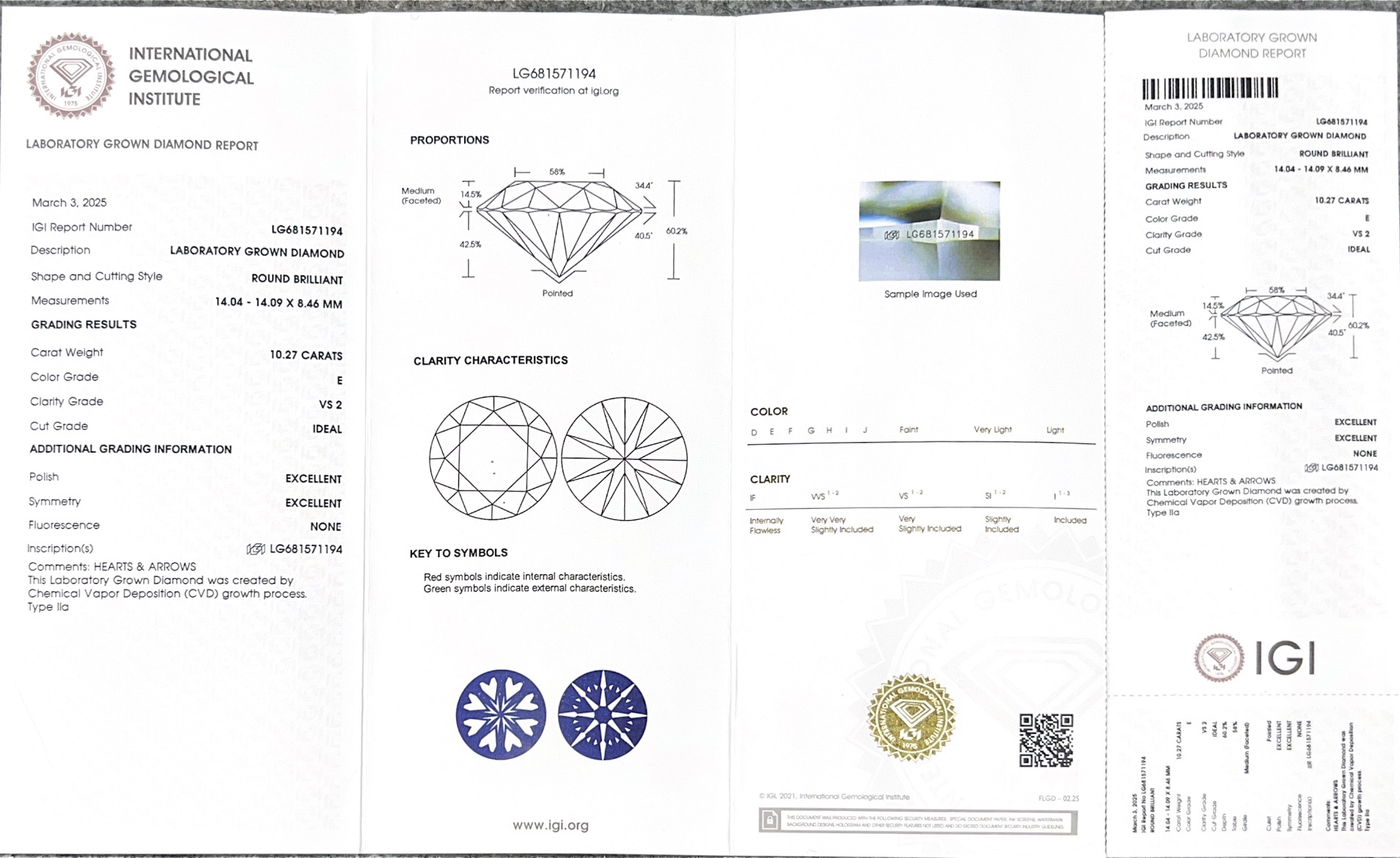
Lab grown diamond IGI Certificate





























